Finance Minister Nirmala Sitharaman presented the Indian Defence Budget for the Financial Year 2026 on 27 February 1, 2026.

Overall Defence Allocation: A Record Increase
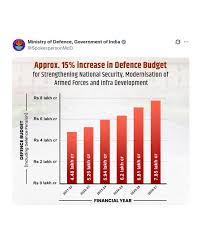
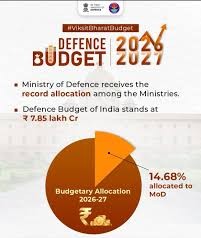
India’s defence spending for FY 2026–27 has been set at approximately ₹7.85 lakh crore, marking a roughly 15% increase over the previous year’s allocation (FY 2025–26: ₹6.81 lakh crore).
Defence remains one of the top-funded ministries in the budget, reflecting strategic priority. This is one of the largest-ever defence outlays in absolute terms.
Defence spending is now close to 1.99%–2.0% of India’s projected GDP, reversing the recent downtrend in the defence-to-GDP ratio.
Maintaining near-2% of GDP aligns India with many major powers and signals sustained political backing for defence preparedness.

Strategic Drivers Behind the Budget
The Budget is the first after Operation Sindoor.
Rising tensions with China and Pakistan, and an evolving security environment, have pressured India to enhance deterrence and capability.
Capital vs Revenue Expenditure: Modernisation Takes Priority
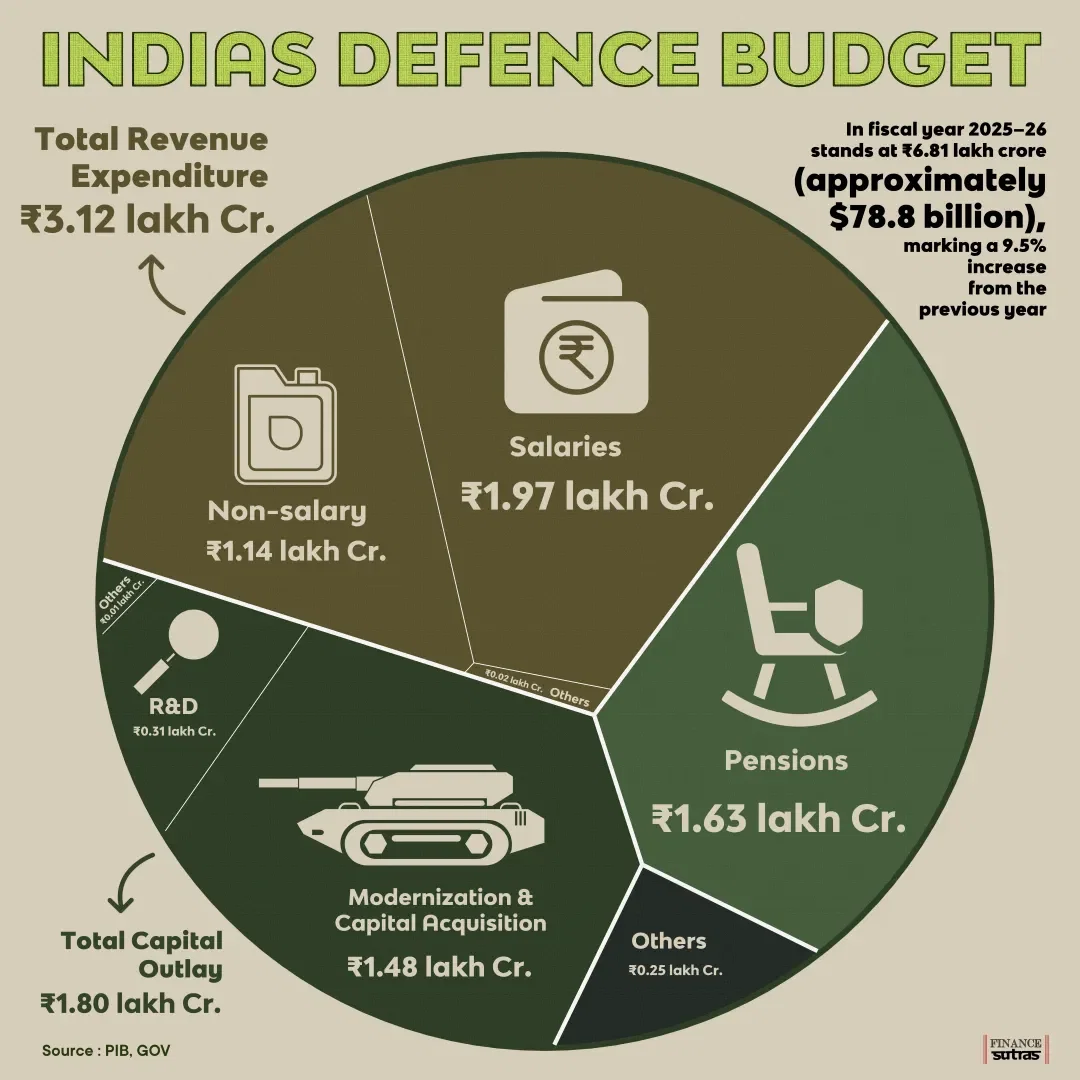
Capital allotment is ₹2.19 lakh crore, up around 22%.
Supports next-gen fighter jets, drones, submarines, and emergency arms post-Operation Sindoor.
Central allocations within this include ₹63,733 crore for aircraft & aero engines and ₹25,023 crore for strengthening the naval fleet.
Also, ₹0.29 lakh crore for DRDO (up from ₹0.27 lakh crore) and ₹0.07 lakh crore for Border Roads Organisation (BRO).
Emergency Procurements: Significant funds are earmarked to replenish stockpiles (ammunition, spares, and fuel) depleted during Operation Sindoor.
This shows a strong push to modernise armed forces, including fighter jets, aeroengines, naval platforms, and unmanned systems, all of which are vital to addressing future capability gaps.

Revenue Expenditure (Operations & Pensions)
Revenue expenditure (payroll, maintenance, operations) remains the bulk of the budget, including ₹1.71 lakh crore for pensions and other recurring costs.
Revenue Expenditure: 3.6546, 57% (20.17% for sustenance/ops + 26.40% for pay/allowances) ₹1.58 lakh crore for operations, maintenance, stores, and spares. Up 17.24% from FY 2025-26 BE, emphasising operational readiness.
Pensions: 1.712, 84% for over 34 lakh pensioners via SPARSH system. Up 6.56% from FY 2025-26 BE. Other (Civil Organisations, ECHS, etc.) 0.29 (approx.)3.64%Includes ₹0.12 lakh crore for Ex-Servicemen Contributory Health Scheme (ECHS), up 45.49% from FY 2025-26 BE and over 300% from FY 2021-22.
Agnipath Scheme: Allocation for the scheme surged by 51% (to ₹15,173 crore), signalling the maturing of the new HR model for the armed forces.
Boost to Self-Reliance (Atmanirbhar Bharat)
This budget reflects a strategic shift towards self-reliance (Aatmanirbhar Bharat), with 75% of capital acquisitions earmarked for domestic industries, including private sector involvement.
It also includes provisions for emergency procurements post-Operation Sindoor, enhanced R&D, and the development of border infrastructure.
Customs Duty Exemptions: Basic Customs Duty (BCD) is waived on raw materials and components imported for the manufacture and maintenance of aircraft parts, as well as for Maintenance, Repair, and Overhaul (MRO).
Impact: This is designed to lower input costs for Defence PSUs and private players, thereby turning India into a regional hub for aircraft maintenance.
The defence budget-linked allocation supports indigenous manufacturing and R&D.
DRDO & iDEX: The R&D budget increase supports next-gen tech like swarm drones, AI-enabled electronic warfare (EW), and hypersonic missiles.
The budget reinforces India’s technology and production push in semiconductors, deep-tech systems, and defence industrial corridors.
This dovetails with broader reform goals, reducing import dependence while strengthening domestic defence firms.
Border Infrastructure (BRO)
Reflecting the tense multi-front reality (China, Pakistan, and Bangladesh), the Border Roads Organisation (BRO) saw its capital budget hiked to ₹7,394 crore. This will accelerate “last-mile connectivity” projects like the Shinku La tunnel and strategic airfields in Ladakh and Arunachal Pradesh.
Intelligence and Internal Security Buildup
The Intelligence Bureau (IB) received a 63% increase in funding, one of the most significant boosts for internal security.
This reflects recognition that modern defence is not just about external threats but also about internal threat management, cyber, intelligence, counter-terrorism, and hybrid warfare.
Analysis and Implications
The budget effectively balances immediate tactical needs (post-Op Sindoor replenishment) with long-term structural shifts (domestic MRO and 75% indigenous procurement).
This budget signals a proactive stance on national security, with the sharpest hikes in capital (21.84%) and revenue (17.24%) outpacing pensions (6.56%), indicating a pivot from legacy costs to future capabilities.
The emphasis on domestic procurement (75% of capital acquisitions) aligns with the Aatmanirbhar Bharat initiative, potentially boosting local industries, job creation, and ancillary sectors like aerospace and electronics.
Post-Operation Sindoor, allocations for emergency arms, drones, and border infrastructure (via BRO) address immediate threats from Pakistan. At the same time, long-term R&D investments (DRDO hike) aim to counter broader challenges from China.
Economically, the 2% GDP share remains below global peers like the US (3.5%) or Russia (4%), but the absolute increase to ~$86 billion positions India as a top (fourth-highest) global spender.
Overall, this allocation enhances India’s deterrence credibility, fosters innovation, and supports regional stability, though sustained execution will be key to realising these goals.
Strategic Takeaways
The most significant increase in defence spending in recent years
Focus on modernisation & capital acquisition.
Alignment with security imperatives post-Operation Sindoor
Growth of the domestic defence ecosystem & R&D push.
Please Add Value to the write-up with your views on the subject.
For regular updates, please register your email here:-
References and credits
To all the online sites and channels.
Pics Courtesy: Internet
Disclaimer:
Information and data included in the blog are for educational & non-commercial purposes only and have been carefully adapted, excerpted, or edited from reliable and accurate sources. All copyrighted material belongs to respective owners and is provided only for wider dissemination.



