John Richard Boyd (January 23, 1927 – March 9, 1997) was a United States Air Force fighter pilot and Pentagon consultant in the second half of the 20th century.
Boyd’s key concept was that of the decision cycle or OODA loop, the process by which an entity (either an individual or an organization) reacts to an event.
Genesis
In the era of 1950s air warfare, there was a peculiar anomaly. In dog fights between MiG-15s and F-86s, the plane that was expected to win (the MiG-15) constantly lost. To explore this, Colonel John Boyd (one of the best Air Force pilots in history) decided to research and get to the root of the situation. The question was, how could an inferior aircraft win so decisively?
Boyd’s Analysis: The reason, he concluded, was something that nobody had thought was particularly important. It was the fact that the F-86 Sabre had a hydraulic flight stick whereas the MiG-15 had a manual flight stick. Without hydraulics, it took slightly more physical energy to move the MiG-15 flight stick than it did the F-86 flight stick. Even though the MiG-15 would turn faster (or climb higher) once the stick was moved, the amount of energy it took to move the stick was greater for the MiG-15 pilot. With each iteration, the MiG-15 pilot grew a little more fatigued than the F-86 pilot. And as he got more fatigued, it took just a little bit longer to complete his OODA loop. The MiG-15 pilot didn’t lose because he got outfought. He lost because he got out-OODAed.
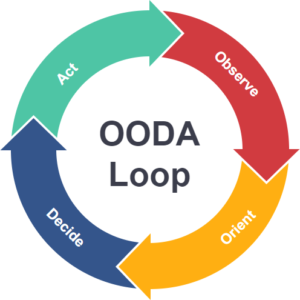
These insights lead us to Boyd’s Theory of OODA LOOP. In the aerial dogfight, the loop looks like this…
Observe the other aircraft
Orient yourself by analyzing the situation
Decide what to do
Act (steer or fire)
OODA Cycle Theory.
Boyd hypothesized that all intelligent organisms and organizations undergo a continuous cycle of interaction with their environment. Boyd breaks this cycle down to four interrelated and overlapping processes through which one cycles continuously:
- Observation: the collection of data by means of the senses
- Orientation: the analysis and synthesis of data to form one’s current mental perspective
- Decision: the determination of a course of action based on one’s current mental perspective
- Action: the physical playing-out of decisions
This decision cycle is thus known as the OODA loop. Boyd theorized that large organizations such as corporations, governments, or militaries possessed a hierarchy of OODA loops at tactical, grand-tactical (operational art), and strategic levels. It is relevant to any kind of competitive environment: business, politics, sports, even the struggle of organisms to survive.
References:
https://www.linkedin.com/pulse/research-reveals-four-steps-learn-faster-better-than-everyone
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/John_Boyd_(military_strategist)
Pic Courtesy: https://online.visual-paradigm.com/knowledge/decision-analysis/what-is-ooda-loop/