Defining DT
A digital twin is a digital representation that functions as a shadow/twin of a physical object or process.
The core idea behind Digital twins is to create a virtual model that incorporates all the necessary information about a physical ecosystem to solve a particular problem.
Digital twins are designed to model and simulate a process to understand it and predict its behaviour.
There is no standard definition of a Digital Twin but it can be defined as a bi-directional data link as well as a data processing entity that simulates, forecasts, and regulates a system in real-time and also transfers and stores data.
Components of Digital Twins
The basic idea of DT is quite straightforward, linking a physical object to a digital entity through a framework comprising at least the following components:
- Data Link
- Coupling (a two-way interface)
- Identifier
- Security
- Data Storage
- User Interface
- Simulation
- Analysis
- Artificial Intelligence
- Computation
Utility
Digital twin originated from engineering and is related to model-based systems engineering (MBSE) and surrogate modelling.
The usage of digital twins is now more mainstream in software development.
Once the system is modelled as a twin, various existing and new engineering problems can be modelled and simulated, such as predictive maintenance, anomaly detection, etc.
Digital twins can be combined with Augmented Reality and Virtual Reality to model physical processes.
Digital Twins will have a big role in enhancing Model-based Design and simulation and will extend to AR (Augmented Reality) and VR (Virtual Reality).
Digital twins have a large scope in design and simulation.
This technology will have a significant impact over the next few years.
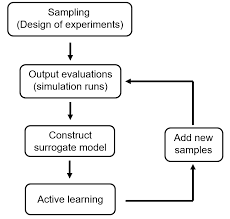
Surrogate model.
Definition. It is an engineering method used when an outcome of interest cannot be easily directly measured, so a model of the outcome is used instead. For example, in order to find the optimal aerofoil shape for an aircraft wing, an engineer simulates the airflow around the wing for different shape variables (length, curvature, material, ..).
For many real-world problems, a single simulation can take many hours, or even days to complete. As a result, routine tasks such as design optimization, design space exploration, sensitivity analysis and what-if analysis become impossible since they require thousands or even millions of simulation evaluations.
One way of alleviating this burden is by constructing approximation models, known as surrogate models, metamodels or emulators, that mimic the behavior of the simulation model as closely as possible while being computationally cheap(er) to evaluate.
Surrogate models are constructed using a data-driven, bottom-up approach. The exact, inner working of the simulation code is not assumed to be known (or even understood), solely the input-output behavior is important.
A model is constructed based on modeling the response of the simulator to a limited number of intelligently chosen data points. This approach is also known as behavioral modeling or black-box modeling, though the terminology is not always consistent.
Though using surrogate models in lieu of experiments and simulations in engineering design is more common, surrogate modelling may be used in many other areas of science where there are expensive experiments and/or function evaluations.
DT vis-à-vis SM
Digital Twin (DT) is a Physics based model, whereas, Surrogate Model (SM) is a Data based model.
DT is good in the parameter-space represented by physics equations, whereas, SM is good in the parameter-space represented by data, but not covering the space represented by equations
Some Interesting Terminologies
Artificial Intelligence (AI). A variety of machine learning and deep learning techniques are collectively referred to as AI.
Virtual Reality (VR). creates an immersive experience through VR devices like headsets and simulates a three-dimensional world. VR is used in instructional content and educational material for field workers, oil and gas, defence, aviation, etc.
Augmented Reality (AR). overlays digital information on a physical world. Typically, AR uses conventional devices like mobile phones.
Mixed Reality (MR). allows the manipulation of both physical and digital objects in an immersive world.
Model-based design. A set of technologies and techniques that help engineers and scientists to design and implement complex, dynamic, end-to-end systems using a set of virtual (digital) modelling technologies. Collectively, these technologies can simulate and model physical objects and processes in multiple industries.
Additive Manufacturing. In the AM approach, first a digital 3D design is created from which the component is printed. The term Additive manufacturing (AM) is used to refer to how technologies like 3D printing are impacting manufacturing. Once the model is digitised, it can be optimised using topology optimization techniques.
Bottom Line
Technology makes the imagination of today into reality of tomorrow.
Technology is a two edged sword – can be used in Civil & Military domain.
Suggestions and value additions are most welcome
For regular updates, please register here
Subscribe
References and credits
To all the online sites and channels.
Disclaimer:
Information and data included in the blog are for educational & non-commercial purposes only and have been carefully adapted, excerpted, or edited from sources deemed reliable and accurate. All copyrighted material belongs to respective owners and is provided only for purposes of wider dissemination.



